geoscientificInformation
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The Geological Survey of Finland (GTK) has carried out systematic aerogeophysical low-altitude surveys during the period 1972-2007. The flight altitude (main terrain clearance) has been 30-40 m with a nominal flight line spacing of 200 m. The standard flight lines chosen run North-South and East-West and follow the main geological trends. The distance between the measuring points along the survey lines has been 6-50 m. The geophysical parameters measured include Earth's magnetic field, the electromagnetic field and natural gamma radiation. Magnetic measurements determine the Earth's magnetic field strength (magnetic flux density), and the parameter obtained is the total magnetic intensity. The measurements have been made with one to three proton magnetometers until 1991 and thereafter with one or two cesium magnetometers. Most of the land area has been flown using two magnetometers.
-
The Regional Stream Sediment Geochemical Mapping data set gives information on the elemental concentrations in organic sediments of small headwater streams. The samples have been taken from small headwater streams (catchment area under 30 km2) in the late summer of 1990. Sampling has been repeated for about every fourth point during the years 1995, 2000 and 2006. The number of samples was 1162 in 1990 (at a density of one sample / 300 km2), 286 in 1995, 286 in 2000 and 249 in 2006. The data set covers the whole of Finland. Stream water samples have also been taken at the same time. Sampling, processing and analysis methods have been described in the Geochemical Atlas of Finland, Part 3, p. 27 - 30 (Lahermo et. al 1996). Field observations, coordinates and element concentrations determined from samples have been made into a database, in which each record represents one sample point. The data for each sampling year have been recorded on different tables. The method of analysis is referred to with a four-character method code. The codes are as follows: 503H = mercury determination using the cold vapour method 503P = nitric acid extraction in a microwave oven, measurement with ICP-AES 503M = nitric acid extraction in a microwave oven, measurement with ICP-MS 820L = carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen determination with a LECO analyser. The element concentration data include a numerical concentration value (as mg kg-1 or ppm) and possibly a check mark. The concentration is recorded as a variable, which has a name that comprises the chemical symbol for the element and the code for the method of analysis. For example AS_503M is arsenic (As) concentration, which is determined with the ICP-MS method (503M). The next variable has a check mark, for example AS_503MT. If the numerical value following the check mark is ‘>’ or '‘<’ then the number recorded in the concentration field is the determination limit of the chemical analytical method used and the actual concentration is less than this value. If the check mark is an exclamation mark (!), the analytical result is smaller than the determination limit of the analytical method use but the (unreliable) value obtained with the measuring instrument has been entered in the database. There is no data are if the check mark is a 'x'. The original purpose of the Regional Stream Water Geochemical Mapping data set was national general geochemical mapping and the basic assessment of environmental state. Other uses are, for example, the assessment of changes in environmental state and determination of the baseline concentrations of surface water as part of the evaluation of the chemical state of catchment areas in accordance with the Water Framework Directive of the EU. The original purpose of the Regional Stream Water Geochemical Mapping data set was national general geochemical mapping and the basic assessment of environmental state. Other uses are, for example, the assessment of changes in environmental state and determination of the baseline concentrations of surface water as part of the evaluation of the chemical state of catchment areas in accordance with the Water Framework Directive of the EU.
-
The EMODnet (European Marine Observation and Data network) Geology project (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/) collects and harmonizes marine geological data from the European sea areas to support decisionmaking and sustainable marine spatial planning. The partnership includes 39 marine organizations from 30 countries. The partners, mainly from the marine departments of the geological surveys of Europe (through the Association of European Geological Surveys- EuroGeoSurveys), have assembled marine geological information at a scale of 1:1 000 000 from all European sea areas (e.g. the White Sea, Baltic Sea, Barents Sea, the Iberian Coast, and the Mediterranean Sea within EU waters). This data includes the EMODnet seabed substrate map at a scale of 1:1 000 000 from the European marine areas. Traditionally, European countries have conducted their marine geological surveys according to their own national standards and classified substrates on the grounds of their national classification schemes. These national classifications are harmonized into a shared EMODnet schema using Folk's sediment triangle with a hierarchy of 16, 7 and 5 substrate classes. The data describes the seabed substrate from the uppermost 30 cm of the sediment column. In cases, the data has been generalized into a target scale (1:1 000 000). The smallest cartographic unit within the data is 4 km2. Further information about the EMODnetGeology project is available on the portal (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/).
-
The EMODnet (European Marine Observation and Data network) Geology project collects and harmonizes marine geological data from the European sea areas to support decision making and sustainable marine spatial planning. The partnership includes 39 marine organizations from 30 countries. The partners, mainly from the marine departments of the geological surveys of Europe (through the Association of European Geological Surveys-EuroGeoSurveys), have assembled marine geological information at various scales from all European sea areas (e.g. the White Sea, Baltic Sea, Barents Sea, the Iberian Coast, and the Mediterranean Sea within EU waters). This dataset includes EMODnet seabed substrate maps at a scale of 1:5 000 from the European marine areas. Traditionally, European countries have conducted their marine geological surveys according to their own national standards and classified substrates on the grounds of their national classification schemes. These national classifications are harmonised into a shared EMODnet schema using Folk's sediment triangle with a hierarchy of 16, 7 and 5 substrate classes. The data describes the seabed substrate from the uppermost 30 cm of the sediment column. Further information about the EMODnet Geology project is available on the portal (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/).
-
The Regional Stream Water Geochemical Mapping data set gives information on the elemental concentrations in organic sediments of small headwater streams. The samples have been taken from small headwater streams (catchment area under 30 km2) in the late summer of 1990. Sampling has been repeated for about every fourth point during the years 1995, 2000 and 2006. The number of samples was 1162 in 1990 (at a density of one sample / 300 km2), 286 in 1995, 286 in 2000 and 249 in 2006. The data set covers the whole of Finland. Stream water samples have also been taken at the same time. Sampling, processing and analysis methods have been described in the Geochemical Atlas of Finland, Part 3, p. 27 - 30 (Lahermo et. al 1996). Field observations, coordinates and element concentrations determined from samples have been made into a database, in which each record represents one sample point. The data for each sampling year have been recorded on different tables. The method of analysis is referred to with a four-character method code. The codes are as follows: 503H = mercury determination using the cold vapour method 503P = nitric acid extraction in a microwave oven, measurement with ICP-AES 503M = nitric acid extraction in a microwave oven, measurement with ICP-MS 820L = carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen determination with a LECO analyser. The element concentration data include a numerical concentration value (as mg kg-1 or ppm) and possibly a check mark. The concentration is recorded as a variable, which has a name that comprises the chemical symbol for the element and the code for the method of analysis. For example AS_503M is arsenic (As) concentration, which is determined with the ICP-MS method (503M). The next variable has a check mark, for example AS_503MT. If the numerical value following the check mark is ‘>’ or '‘<’ then the number recorded in the concentration field is the determination limit of the chemical analytical method used and the actual concentration is less than this value. If the check mark is an exclamation mark (!), the analytical result is smaller than the determination limit of the analytical method use but the (unreliable) value obtained with the measuring instrument has been entered in the database. There is no data are if the check mark is a 'x'. The original purpose of the Regional Stream Water Geochemical Mapping data set was national general geochemical mapping and the basic assessment of environmental state. Other uses are, for example, the assessment of changes in environmental state and determination of the baseline concentrations of surface water as part of the evaluation of the chemical state of catchment areas in accordance with the Water Framework Directive of the EU.
-
The EMODnet (European Marine Observation and Data network) Geology project collects and harmonizes marine geological data from the European sea areas to support decision making and sustainable marine spatial planning. The partnership includes 39 marine organizations from 30 countries. The partners, mainly from the marine departments of the geological surveys of Europe (through the Association of European Geological Surveys-EuroGeoSurveys), have assembled marine geological information at various scales from all European sea areas (e.g. the White Sea, Baltic Sea, Barents Sea, the Iberian Coast, and the Mediterranean Sea within EU waters). This dataset includes EMODnet seabed substrate maps at a scale of 1:60 000 from the European marine areas. Traditionally, European countries have conducted their marine geological surveys according to their own national standards and classified substrates on the grounds of their national classification schemes. These national classifications are harmonised into a shared EMODnet schema using Folk's sediment triangle with a hierarchy of 16, 7 and 5 substrate classes. The data describes the seabed substrate from the uppermost 30 cm of the sediment column. Further information about the EMODnet Geology project is available on the portal (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/).
-
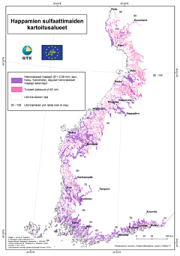
The data on acid sulfate soils in 1:250 000 scale contains material generated since 2009 on the existence and properties of sulfate soils on the Finnish coastal areas and their drainage basins roughly up to the highest shoreline of the ancient Litorina Sea. The data contains the following levels: - Acid sulfate soils, 1:250 000 maps o Probability of the existence of acid sulfate soils o Probability of the existence of coarse-grained acid sulfate soils - Acid sulfate soils, profile points on 1:250 000 maps - Acid sulfate soils, survey points on 1:250 000 maps - Acid sulfate soils, profile point fact sheets on 1:250 000 maps The data gives a general outlook on the properties and occurrence of acid sulfate soils. The regional existence of sulfate soils is presented as a regional map plane using a four-tiered probability classification: high, moderate, low and very low. These classifications are complemented with regional planar data on whether the acid sulfate soil is coarse-grained, since its properties are significantly different from typical fine-grained sulfate soils. The drilling point (profile points and survey points) observations and analysis data are presented as point-like data on the map and as profile point fact sheets linked to points The survey data can be utilised, for example, in the planning and execution of land use and water management as required by environmental protection and land use. The survey scale is 1:20 000 – 1:50 000. The observation point density is 1–2 / 2 km² on average, and the minimum area of the region-like pattern is usually 6 hectares. The surveys collected data on the lithostratigraphy, existence of sulfide and the depth where found, and the soil pH values. The survey depth is three metres. The laboratory analyses included the determination of elements with the ICP-OES method and pH incubation. The data is published in GTK’s Acid Sulfate Soils map service.
-
The GTK’s Mineral Deposit database contains all mineral deposits, occurrences and prospects in Finland. Structure of the new database was created in 2012 and it is based on global geostan-dards (GeoSciML and EarthResourceML) and classifications related to them. The database is in Oracle, data products are extracted from the primary database. During 2013 GTK’s separate mineral deposit databases (Au, Zn, Ni, PGE, U, Cu, Industrial minerals, FODD, old ore deposit database) were combined into a single entity. New database contains extensive amount of information about mineral occurrence feature along with its associated commodities, exploration activities, holding history, mineral resource and re-serve estimates, mining activity, production and geology (genetic type, host and wall rocks, min-erals, metamorphism, alteration, age, texture, structure etc.) Database will be updated whenever new data (e.g. resource estimate) is available or new deposit is found. Entries contain references to all published literature and other primary sources of data. Also figures (maps, cross sections, photographs etc.) can be linked to mineral deposit data. Data is based on all public information on the deposits available including published literature, archive reports, press releases, companies’ web pages, and interviews of exploration geologists. Database contains 33 linked tables with 216 data fields. Detailed description of the tables and fields can be found in separate document. (http://tupa/metaviite/MDD_FieldDescription.pdf) The data products extracted from the database are available on Mineral Deposits and Exploration map service (http://gtkdata.gtk.fi/MDaE/index.html) and from Hakku -service (http://hakku.gtk.fi).
-
The EMODnet (European Marine Observation and Data network) Geology project (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/) collects and harmonizes marine geological data from the European sea areas to support decision- making and sustainable marine spatial planning. The partnership includes 36 marine organizations from 30 countries. The partners, mainly from the marine departments of the geological surveys of Europe (through the Association of European Geological Surveys-EuroGeoSurveys), have assembled marine geological information at a scale of 1:250 000 from all European sea areas (e.g. the White Sea, Baltic Sea, Barents Sea, the Iberian Coast, and the Mediterranean Sea within EU waters). This data includes the EMODnet seabed substrate map at a scale of 1:250 000 from the European marine areas. Traditionally, European countries have conducted their marine geological surveys according to their own national standards and classified substrates on the grounds of their national classification schemes. These national classifications are harmonized into a shared EMODnet schema using Folk's sediment triangle with a hierarchy of 16, 7 and 5 substrate classes. The data describes the seabed substrate from the uppermost 30 cm of the sediment column. The data has been generalized into a target scale (1:250 000). The smallest cartographic unit within the data is 0.3 km2 (30 hectares). Further information about the EMODnet-Geology project is available on the portal (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/).
-
Seabed substrate 1:100 000 is one of the products produced in the EMODnet (European Marine Observation and Data network) Geology III EU project. Project provided seabed geological material from the European maritime areas. The EMODnet Geology III project (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/) collects and harmonizes geological data from the European sea areas to support decision-making and sustainable marine spatial planning. The EMODnet Geology partnership has included 39 marine organizations from 30 countries. This data includes the EMODnet seabed substrate map at a scale of 1:100 000 from the Finnish marine areas. It is based on the data produced on a scale of 1:20 000 by the Geological Survey of Finland (GTK). The data has been harmonized and reclassified into five Folk substrate classes (clay + silt (mud), sandy clays, clayey sands, coarse sediments, mixed sediments) and bedrock. The data describes the seabed substrate from the uppermost 30 cm of the sediment column. The data have been generalized into a target scale (1:100 000). The smallest smallest cartographic unit within the data is 0.05 km2 (5 hectares). Further information about the EMODnet-Geology project III is available on the portal (http://www.emodnet-geology.eu/). Permission (AN17367) to publish the material was obtained from the Finnish Defence Office 29.9.2017.
 Paikkatietohakemisto
Paikkatietohakemisto